ChE 1101 Fall 2005
IONS:
The building blocks of all matter are atoms. Atoms are composed
of electrons (negative charges), protons (positive charges), and neutrons
(neutral charges). The positive and negative charges are
balanced (or equal) in a neutral atom. The protons and neutrons
are located in the nucleus while the electrons are located in orbital “clouds” around
the nucleus. The protons remain in the nucleus throughout chemical
reactions, but the electrons can be lost or gained fairly easily. When
these negative charges are either added or removed, a charged ion is
formed. Read more at: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/atom_ions.html An
atom that has lost a negative charge becomes an ion with a net positive
charge. This is called a cation.
1. An anion is an ion with a net negative charge. What happened
to the original neutral atom to form an anion? ______________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
A sodium atom (Na) can lose and electron to become a cation which we represent with Na+.
| Na atom | Na+ ion (cation) | |
| 11 protons | 11 protons | |
| 11 electrons | 10 electrons | |
| net charge = | 0 |
+1 |
A chlorine atom (Cl) can become an anion (represented by Cl-) in the following manner.
| Cl atom | Cl- ion (anion) | |
| 17 protons | 17 protons | |
| 17 electrons | 18 electrons | |
| net charge = | 0 |
-1 |
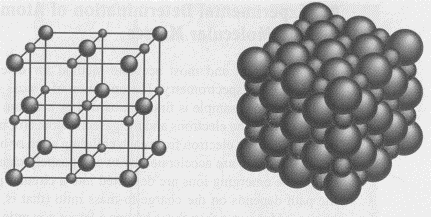
Opposite
charges are attracted to each other so that a stable, neutral
molecule forms. Salts are compounds containing cations
and anions bonded together to form a molecule that readily dissolves
in water. An example of this is sodium chloride (NaCl). The
picture above shows the regular binding of solid NaCl. Have
you ever noticed how table salt is made up of perfect cubes? In
reality, the cations and anions are in direct contact as shown
in the picture at right. The larger spheres are Cl-
and the smaller spheres are Na+.
An atom can lose or gain more than one electron. An example of this is magnesium (Mg +2) or sulfur (S -2). These two can bind together to form magnesium sulfide (MgS). Notice that the charges in the molecule have to balance out too (+2 and –2 for the magnesium sulfide).
2. What happens if a sodium cation wants to bind to a sulfur anion? __________________________________________________________________________
3. What about a magnesium cation binding to a chlorine anion? ________________________________________________________________________
ELECTRICITY

Now we know that electricity can travel through water. Actually,
that isn’t entirely true; pure H2O is a poor conductor
of electricity. But water from your faucet is excellent. This
is because tap water and water found in lakes, rivers, and oceans
contain ions. Electricity is just a flow of electrons or
negative charges. Ever notice how a battery has a negative
end and a positive end and how it won’t work in your radio
if you put it in backwards?
In our next session, we are going to run an electrical current through a salt solution causing ions to move. With a chemical indicator, we will measure the accumulation of ions at the positive and negative electrodes. Please look up the following concepts and provide definitions.
- electricity
- ionic solutions
- electrophoresis
- cathode
- anode
- electrical potential
- electrical field
- mobility
Answers questions (1 through 11) in a Word file and upload onto
webCT under the “Charged up on Electrophoresis” section.
Contact minerick@mtu.edu if
you have any questions.